Murine typhus, a lesser-known but serious flea-borne disease, is caused by the bacteria Rickettsia typhi and transmitted primarily through flea bites. This disease, also known as endemic typhus, often presents symptoms that can be mistaken for other illnesses, leading to underreporting and misdiagnosis. Although it is relatively rare, it can have severe complications if not treated promptly.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about this disease, from its symptoms and transmission to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped with valuable information to protect yourself and your loved ones from this flea-borne disease.
Table of Contents
What is Murine Typhus?
Murine typhus is caused by Rickettsia typhi, a bacterium transmitted to humans through the bites of infected fleas. These fleas typically live on rodents such as rats, but can also be found on pets like cats and dogs. The infection is more common in warm climates, including the southern regions of the United States, but cases have been reported worldwide. It’s important to note that while this disease is often confused with epidemic typhus, they are different diseases, each caused by different bacteria.
How is Murine Typhus Transmitted?
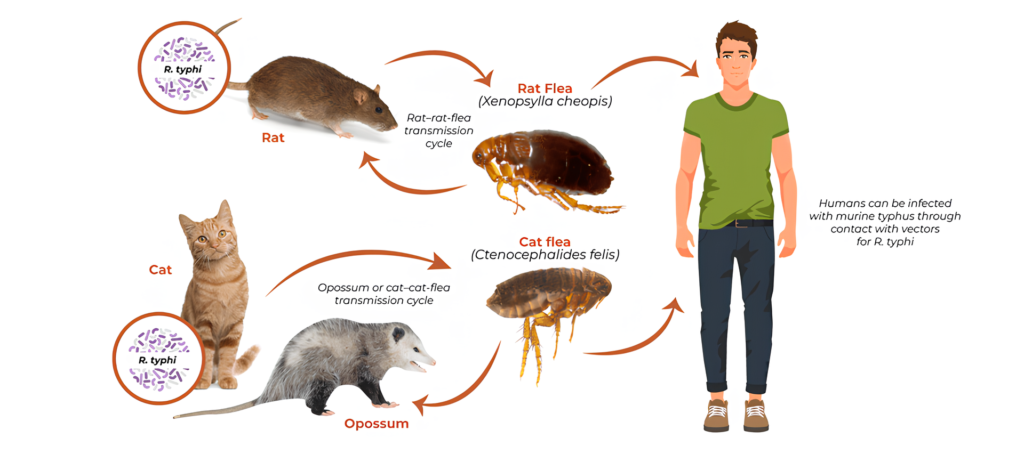
Fleas, particularly those found on rodents, are the primary vectors for this disease. When an infected flea bites a human, the bacteria Rickettsia typhi are introduced into the bloodstream. In some cases, people can become infected through the inhalation of flea feces, which can become airborne when the flea is crushed or disturbed.
Key Points of Transmission:
- Flea bites from infected fleas.
- Exposure to flea feces through scratching or inhalation.
- Close proximity to rodents and other flea hosts.
Living in environments with a high population of rodents or stray animals increases the risk of murine typhus transmission. Urban areas where hygiene and pest control are poor can be breeding grounds for fleas, thus increasing the risk of infection.
Typhus Symptoms: Recognizing the Signs of Murine Typhus
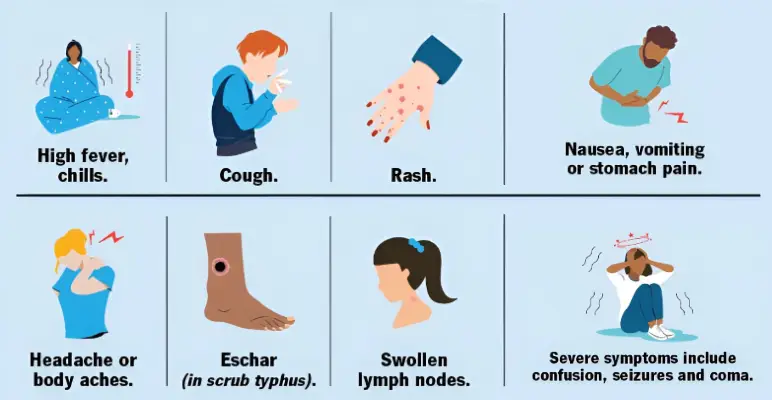
Murine typhus shares symptoms with other infectious diseases, making it difficult to diagnose. Symptoms typically appear within 6-14 days after exposure to infected fleas.
Common Symptoms Include:
- Fever (often high and sudden).
- Headache and muscle aches.
- Rash, usually appearing on the chest, back, or abdomen.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Fatigue and general weakness.
In more severe cases, individuals may experience complications such as respiratory issues or central nervous system involvement, which can lead to confusion or seizures. These symptoms may worsen if the disease is not promptly diagnosed and treated.
Murine Typhus Diagnosis
Diagnosing murine typhus can be challenging because the symptoms resemble other febrile illnesses such as flu or other viral infections. However, doctors may suspect this disease if a patient presents with a combination of symptoms and a history of potential exposure to fleas or rodents.
Diagnosis Methods:
- Blood tests to detect Rickettsia typhi antibodies.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests to identify bacterial DNA.
- Comprehensive medical history including travel or exposure to flea-infested areas.
Early diagnosis is crucial for preventing complications. If this disease is suspected, seeking immediate medical care is recommended to initiate treatment as soon as possible.
Murine Typhus Treatment: What to Expect
The good news is that it is treatable, especially when caught early. The antibiotic doxycycline is the most commonly prescribed medication and is highly effective in eradicating the bacteria. Patients usually see improvement within 48 hours of starting treatment, with a full recovery expected in most cases.
Key Points About Treatment:
- Doxycycline is the first-line treatment for adults and children over eight.
- Recovery time ranges from several days to weeks, depending on severity.
- Early treatment reduces the risk of complications.
In more severe cases or for those allergic to doxycycline, alternative antibiotics such as azithromycin may be prescribed. Treatment is typically short-term, but it’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics to prevent relapse.
Causes of Murine Typhus: Understanding Risk Factors
The root cause of this disease is exposure to fleas infected with Rickettsia typhi. Certain environmental and behavioral factors increase the risk of contracting the disease, particularly in urban areas or places with poor sanitation.
Risk Factors Include:
- Close proximity to rodent populations, especially in urban environments.
- Pet ownership, particularly if pets are exposed to fleas from outdoor animals.
- Traveling to or living in areas with endemic flea populations.
- Poor sanitation or lack of pest control measures.
Understanding these risk factors can help in both prevention and early identification of the disease.
Murine Typhus Prevention: How to Protect Yourself
The best way to prevent it is to minimize exposure to flea vectors. This can be achieved through a combination of personal hygiene, pest control, and responsible pet ownership.
Practical Prevention Tips:
- Control Flea Populations: Use flea control products on pets, and regularly clean bedding and living areas to reduce flea infestations.
- Rodent Control: Seal entry points to your home to prevent rodent infestations, and avoid leaving food sources that may attract rodents.
- Protect Yourself Outdoors: Wear insect repellent when in areas with known flea infestations, and avoid contact with stray animals or wildlife.
- Environmental Sanitation: Keep living areas clean and free from waste, which can attract rodents and their fleas.
Murine Typhus Complications: What You Need to Know
While most cases of it are mild to moderate, complications can arise if the disease is left untreated. Severe complications include:
- Respiratory Issues: Pneumonia and other lung infections.
- Neurological Effects: Confusion, delirium, and even seizures.
- Organ Damage: In rare cases, untreated this disease can lead to organ failure.
These complications are more common in older adults or individuals with weakened immune systems. Timely medical intervention significantly reduces the risk of these outcomes.
Typhus vs. Murine Typhus: What’s the Difference?
While this disease is sometimes referred to as “endemic typhus,” it is different from epidemic typhus, which is caused by Rickettsia prowazekii. Epidemic typhus is more severe and is typically spread by lice, not fleas. Understanding the difference between these two diseases is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Key Differences:
- Epidemic Typhus: Caused by Rickettsia prowazekii, spread by lice, and more deadly.
- Murine Typhus: Caused by Rickettsia typhi, spread by fleas, and generally milder but still serious.
Both diseases share similar symptoms, making medical history and diagnostic testing vital in distinguishing between the two.
FAQ
How is murine typhus transmitted?
Murine typhus is primarily transmitted through the bites of infected fleas, particularly those found on rodents. In some cases, flea feces can infect a person through inhalation or skin contact.
What are the main symptoms of murine typhus?
Symptoms include high fever, headache, rash, nausea, and muscle aches. These symptoms usually appear within 1-2 weeks after exposure to infected fleas.
Is murine typhus dangerous?
While murine typhus can be serious, it is treatable with antibiotics like doxycycline. Severe complications can occur if left untreated, but they are rare with timely treatment.
How can I prevent murine typhus?
Preventing murine typhus involves controlling flea populations, avoiding contact with rodents and stray animals, and maintaining a clean living environment.
Conclusion
Murine typhus, though rare, is a serious flea-borne disease that can lead to severe complications if not treated promptly. By understanding how the disease is transmitted, recognizing its symptoms, and taking preventive measures, you can protect yourself and your family. If you suspect you’ve been exposed, seek medical advice promptly to ensure timely diagnosis and treatment.
Stay informed about health topics by subscribing to our newsletter, and share this post with friends and family to spread awareness!
Get more information on these reliable sources
Read more



